Wood Cutting: CNC Router VS. Laser – Key Differences Explained
Seattle Art & Industrial shapes and cuts wood using two different methods, utilizing its 9′ x 5′ four-axis CNC (Computer Numerical Control) Router or its 10′ x 7′ industrial Laser. Both methods offer precise, CAD (Computer Aided Design) controlled shaping solutions so that you can create and/or reproduce your work, whether it be decorative (e.g. sculpture, design embellishment, etc.) or functional (e.g. furniture, wall panels, signage, etc.).
Below is a quick list of key points explaining the capabilities of each process:
CNC Router Cutting
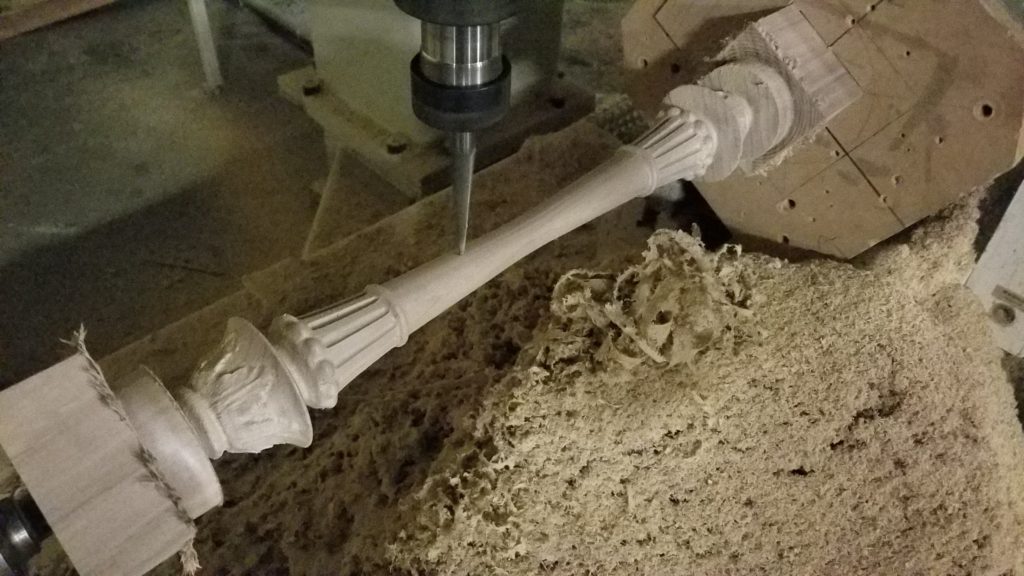
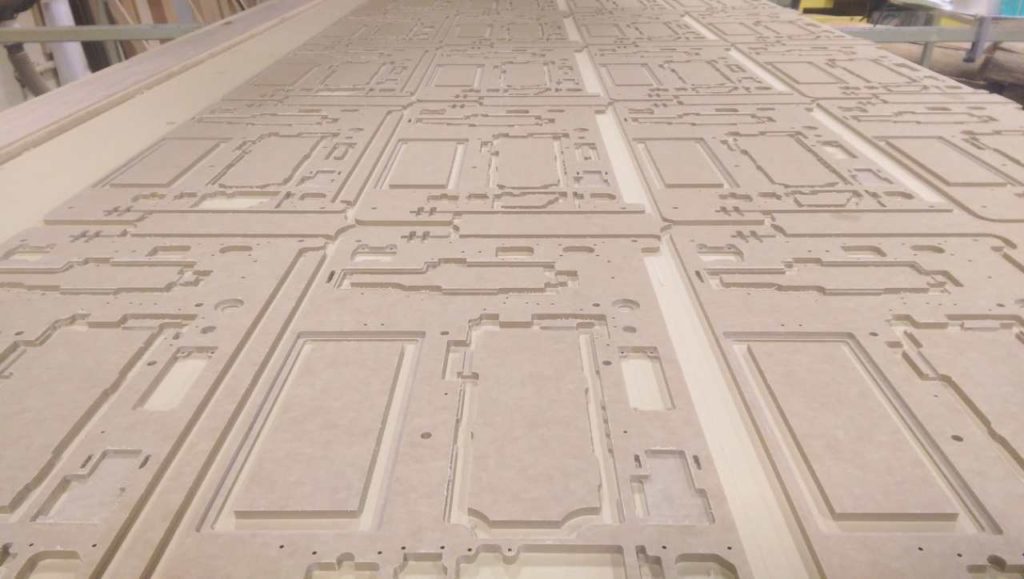
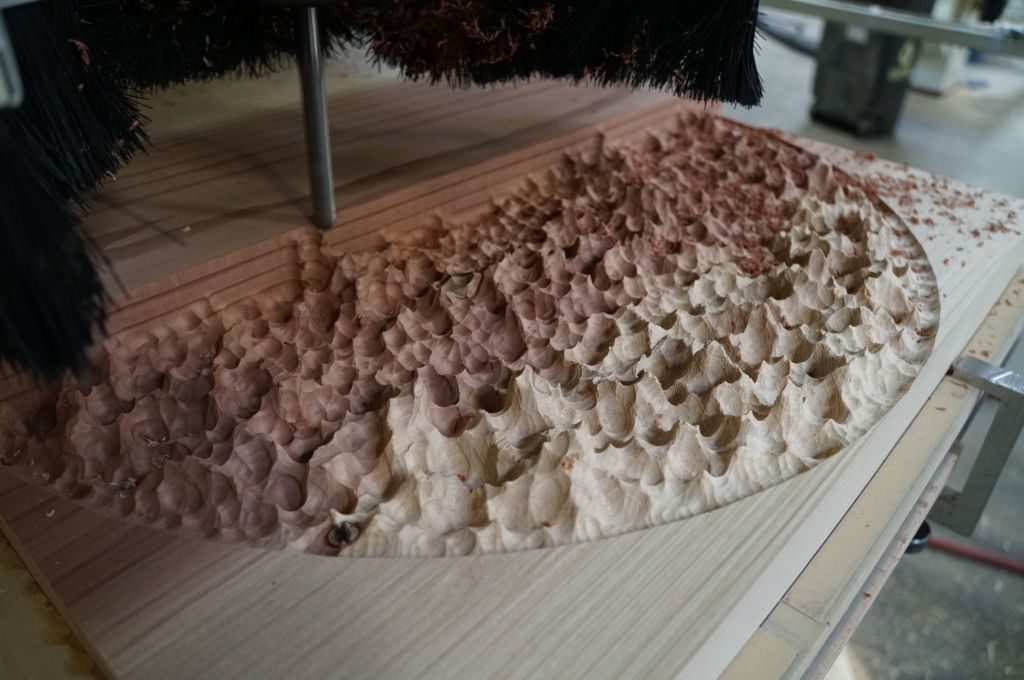
The CNC router:
-
- employs routing “bits” – each one selected as required for the piece from an array of bit shapes and thickness.
- is capable of working with both, 2D and 3D Geometry
- cuts smooth edges without distorting the color of the work
- leaves a small radius in any “inside” geometry that is intended for sharp corners
- can cut up to 6″ deep in one pass
- can easily cut either soft and hard wood in any thickness
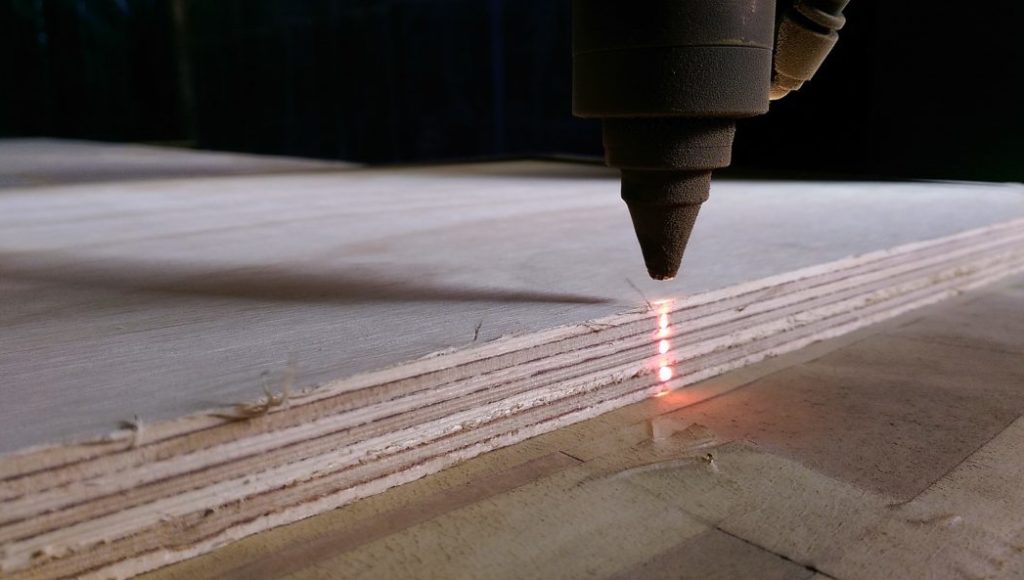
Industrial Laser Cutting
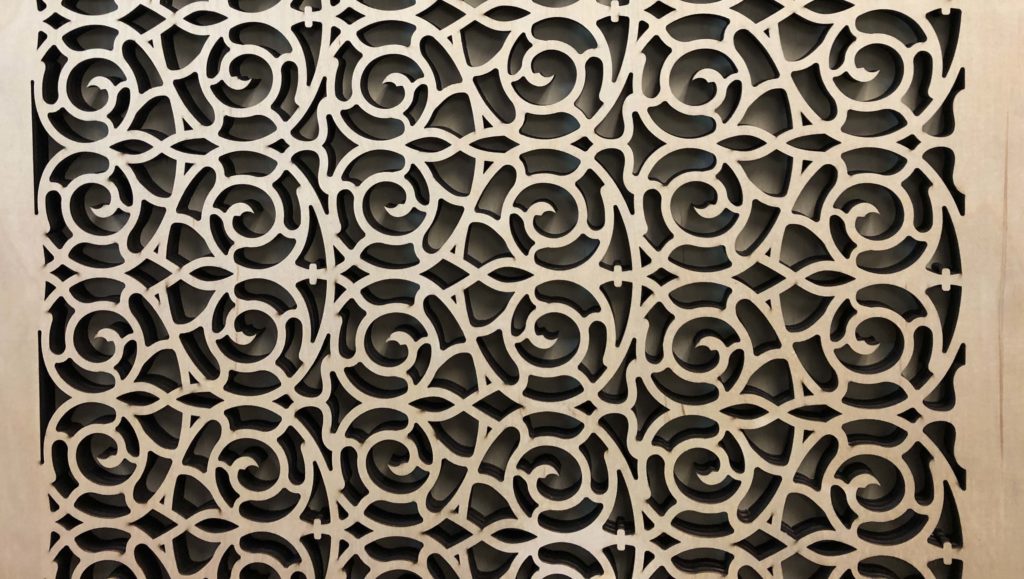
The Industrial Laser:
-
- works with 2D geometry
- is perfect for MDF, Plywood, Richlite, and many other types of wood mostly up to 1″ thick
- requires less programming and is more efficient, and, thus, may be less expensive overall (compared to CNC Router)
- cuts precise crisp and precise edges
- may darken edges, via laser “burning” which may allow patterns to stand out
- is perfect for sharp edge cutting and internal 90 degree corners